When would you want to use it?
Whylogs is an open-source library that analyzes your data and creates statistical summaries called whylogs profiles. Whylogs profiles can be processed in your pipelines and visualized locally or uploaded to the WhyLabs platform, where more in depth analysis can be carried out. Even though whylogs also supports other data types, the ZenML whylogs integration currently only works with tabular data inpandas.DataFrame format.
You should use the whylogs/WhyLabs Data Validator when you need the following data validation features that are possible with whylogs and WhyLabs:
- Data Quality: validate data quality in model inputs or in a data pipeline
- Data Drift: detect data drift in model input features
- Model Drift: Detect training-serving skew, concept drift, and model performance degradation
How do you deploy it?
The whylogs Data Validator flavor is included in the whylogs ZenML integration, you need to install it on your local machine to be able to register a whylogs Data Validator and add it to your stack:How do you use it?
Whylogs’s profiling functions take in apandas.DataFrame dataset generate a DatasetProfileView object containing all the relevant information extracted from the dataset.
There are three ways you can use whylogs in your ZenML pipelines that allow different levels of flexibility:
- instantiate, configure and insert the standard WhylogsProfilerStep shipped with ZenML into your pipelines. This is the easiest way and the recommended approach, but can only be customized through the supported step configuration parameters.
- call the data validation methods provided by the whylogs Data Validator in your custom step implementation. This method allows for more flexibility concerning what can happen in the pipeline step, but you are still limited to the functionality implemented in the Data Validator.
- use the whylogs library directly in your custom step implementation. This gives you complete freedom in how you are using whylogs’s features.
The whylogs standard step
ZenML wraps the whylogs/WhyLabs functionality in the form of a standardWhylogsProfilerStep step. The only field in the step config is a dataset_timestamp attribute which is only relevant when you upload the profiles to WhyLabs that uses this field to group and merge together profiles belonging to the same dataset. The helper function whylogs_profiler_step used to create an instance of this standard step takes in an optional dataset_id parameter that is also used only in the context of WhyLabs upload to identify the model in the context of which the profile is uploaded, e.g.:
pandas.DataFrame dataset, e.g.:
DatasetProfileView object:
The whylogs Data Validator
The whylogs Data Validator implements the same interface as do all Data Validators, so this method forces you to maintain some level of compatibility with the overall Data Validator abstraction, which guarantees an easier migration in case you decide to switch to another Data Validator. All you have to do is call the whylogs Data Validator methods when you need to interact with whylogs to generate data profiles. You may optionally enable whylabs logging to automatically upload the returned whylogs profile to WhyLabs, e.g.:Call whylogs directly
You can use the whylogs library directly in your custom pipeline steps, and only leverage ZenML’s capability of serializing, versioning and storing theDatasetProfileView objects in its Artifact Store. You may optionally enable whylabs logging to automatically upload the returned whylogs profile to WhyLabs, e.g.:
Using the whylogs ZenML Visualizer
In the post-execution workflow, you can load and render the whylogs profiles generated and returned by your pipeline steps by means of the ZenML whylogs Visualizer. The visualizer can take in a single step view, or two separate step views. In the first case, a visualization of a single data profile is rendered, in the second you will get a data drift report, e.g.: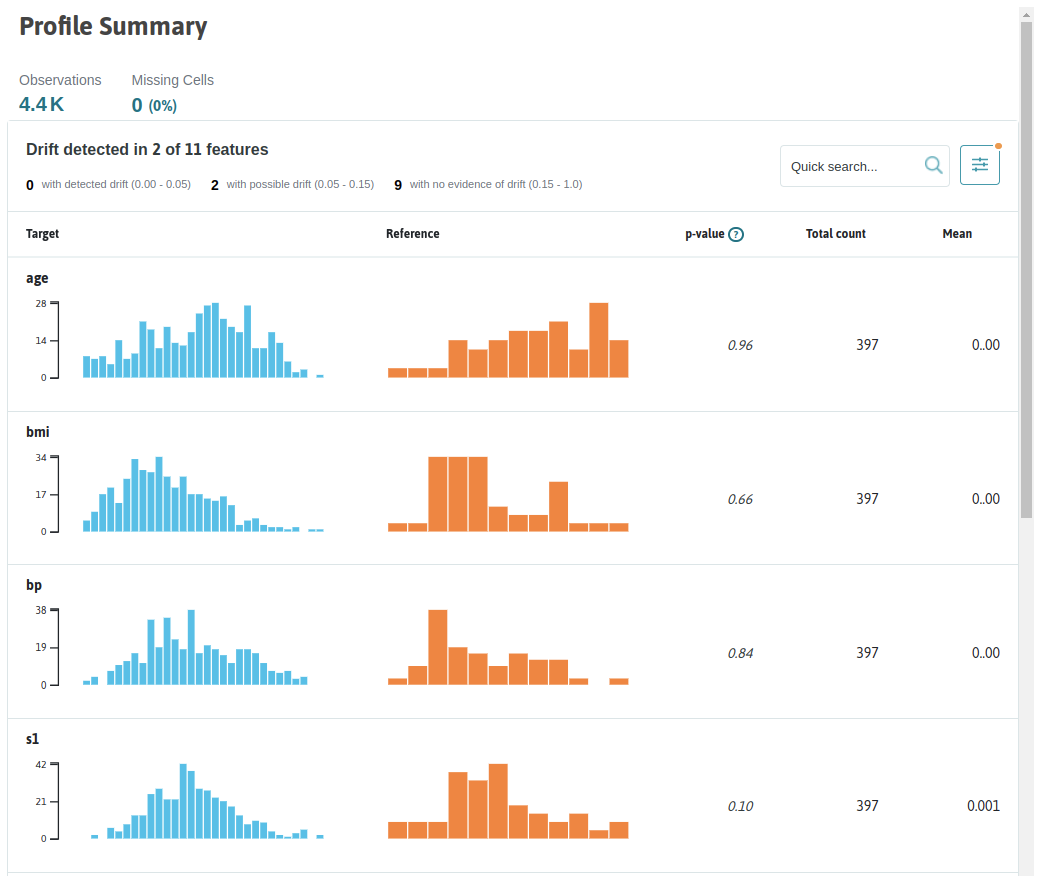 Whylogs Visualization Example 1
Whylogs Visualization Example 1
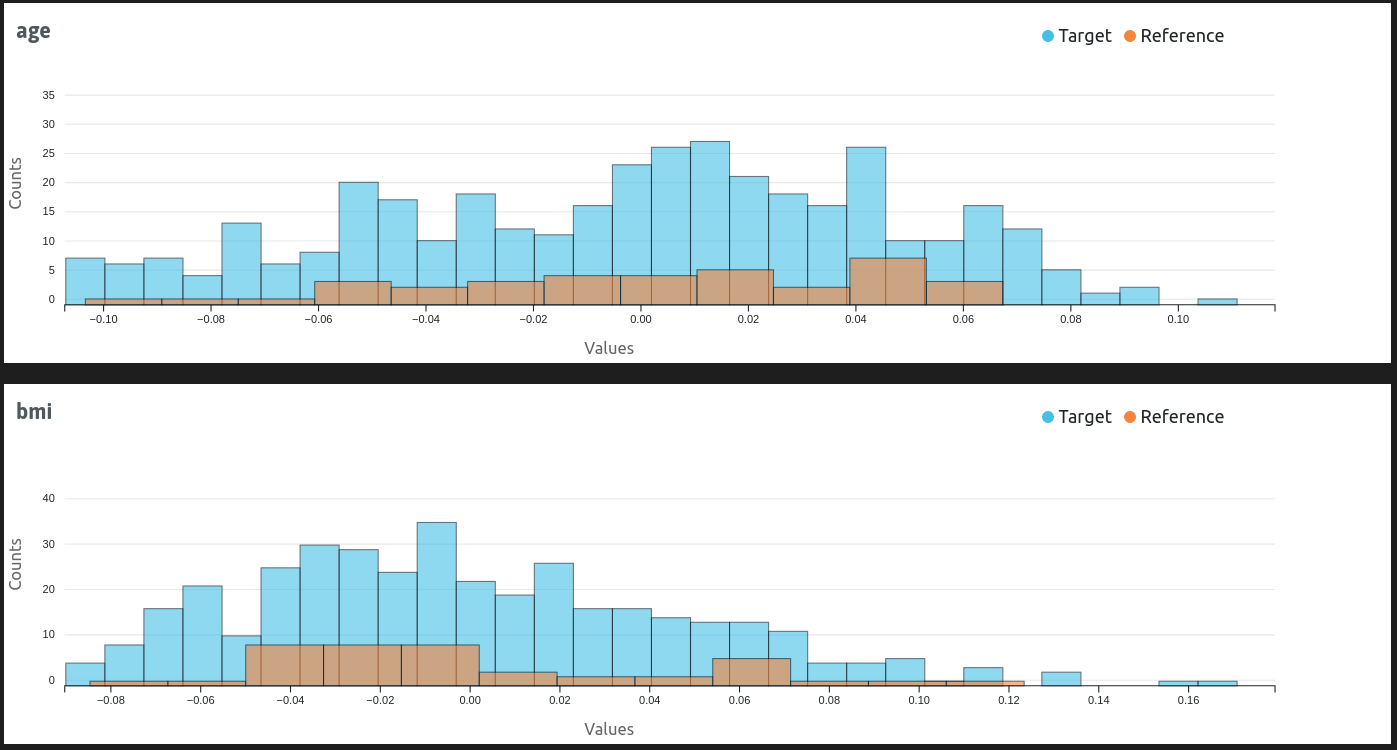 Whylogs Visualization Example 2
Whylogs Visualization Example 2
