Skip to main contentZenML is designed to live at the interface between all the ingredients to your machine learning development environment. As such there is a lot of configuration and metadata to keep track of. This means that ZenML does not only give users an easy-to-use abstraction layer on top of their infrastructure and environments, but also needs to act as a collaborative metadata store. To get a complete overview of the architecture of ZenML, read here.
As with any other service, however, ZenML needs to be deployed first in order to be able to use it. This section covers the various scenarios when it comes to deploying ZenML, from starting locally to transitioning to the cloud.
Tip: In order to skip deploying ZenML completely, or if you just want to get up and running quickly, you can use an early version of the ZenML Cloud where we’ll give you a free and managed ZenML server!
The components of a ZenML Deployment
A ZenML deployment can consist of the following three components:
- The ZenML client.
- A SQL database.
- An optional FastAPI HTTP server that exposes a RESTful API as well as a UI.
ZenML relies on a SQLAlchemy-compatible database to store all its data: stack configurations, pipeline runs etc. The location and type of this database can be freely chosen by the user. By default, a SQLite database is stored on your local host (see Scenario 1).
ZenML can also be deployed with an HTTP REST interface between the client machine and the database. This is also the interface used by the ZenML dashboard when loaded in your browser. Especially in multi-user settings, this is the recommended configuration scenario.
Running ZenML Locally
Running ZenML locally is an easy way to experiment with your pipelines and design proof-of-concepts. Scenarios 1 and 2 below deal with the local deployment of ZenML. In these scenarios, the ZenML client and database are both located on the same machine.
Scenario 1: Direct interaction with Local SQLite
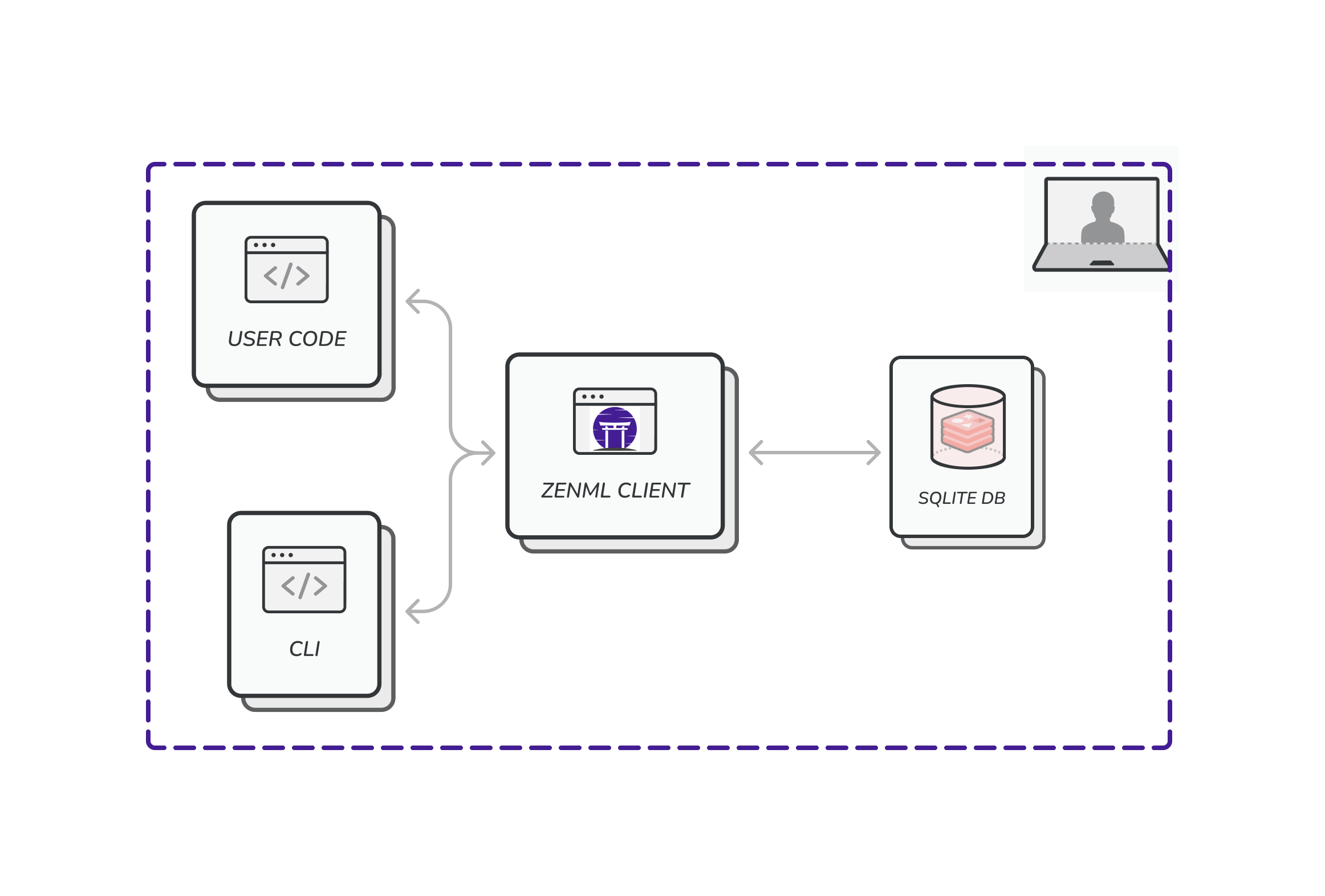
This is likely the first experience that users will run into. Simply pip install zenml and dive right in without having to worry about a thing. Your stacks, stack components and pipeline runs all are stored in a SQLite database located in your global configuration directory (e.g. at ~/.config/zenml/local_stores/default_zen_store/zenml.db if you’re running on Linux). The ZenML client creates and directly connects to this database. You don’t need to worry about a thing.
Users that wish to be fancy about how they connect to the database can find out how to configure a different location for the SQLite database, or even a different database altogether here.
Scenario 2: Local Deployment of the HTTP server
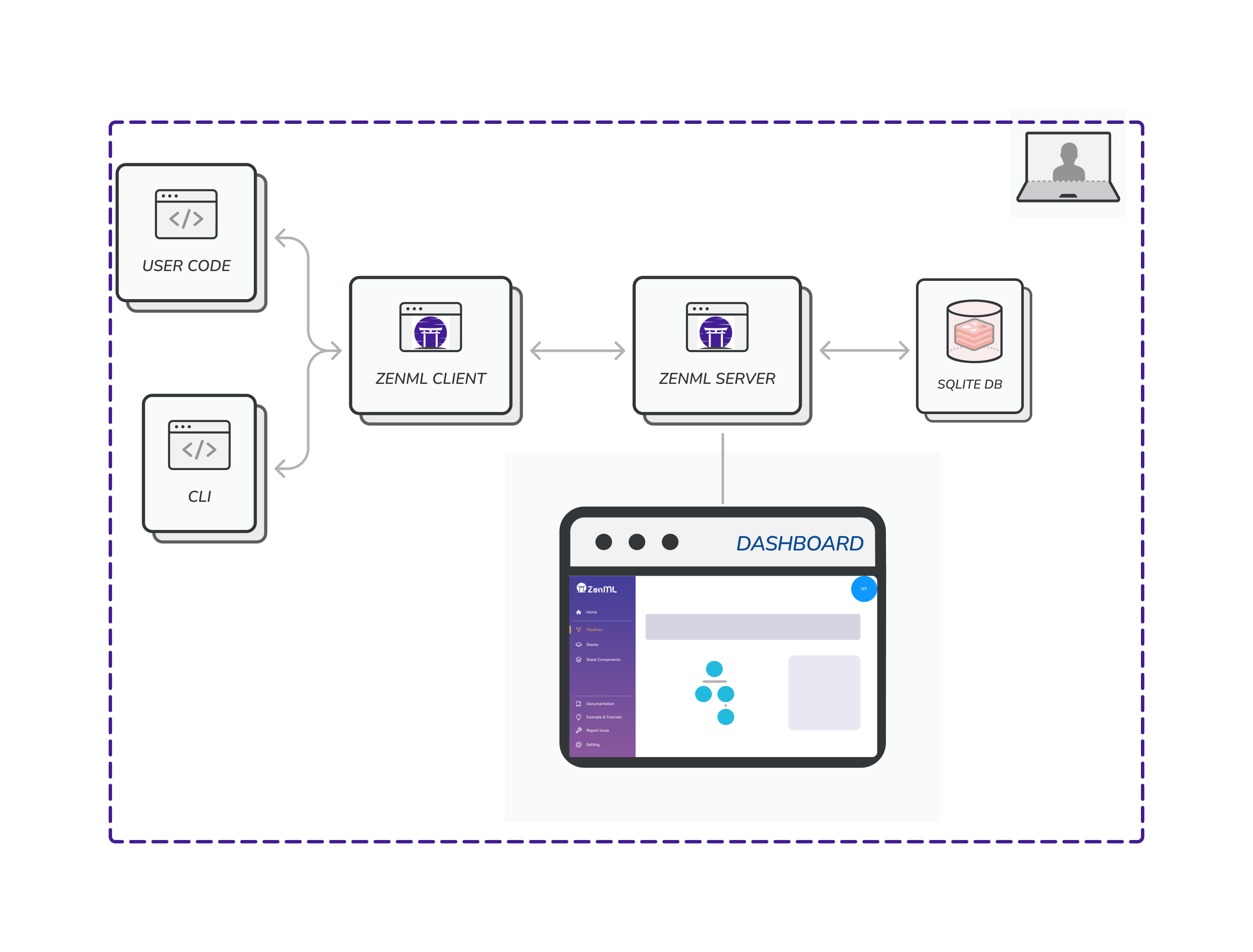
In this use-case, a local version of the ZenML HTTP server is running on your machine and is using the same database as your local client in Scenario 1. All client calls go through REST API endpoints instead of writing directly to the database. This option allows you to visualize and navigate your stacks and tracked pipeline information in the ZenML dashboard.
Switching from Scenario 1 to Scenario 2 and back is as simple as running zenml up and zenml down.
ZenML natively supports running the HTTP server and dashboard either as a process running in the background or as a Docker container. By default, the zenml up command starts the HTTP server as a local daemon process that uses the same database configuration as your local client. A URL is provided where the ZenML Dashboard can be loaded to show your available stacks, pipeline runs and team settings among other things. If you need to use Docker containers instead, you can find out more about Docker deployments here.
Deploying ZenML in the Cloud: Remote Deployment of the HTTP server and Database
For a lot of use cases like sharing stacks and pipeline information with your team and for using cloud services to run your pipelines, you have to deploy ZenML in the cloud.
Your ZenML code interacts with the server across different concerns. For example,
- your local machine connects to the server to read and write the stack configurations to allow collaboration.
- the individual orchestrators and step operators communicate with the server to write and track your pipeline run data.
- the dashboard is served from the server to give a UI interface to all of your metadata.
As such, it is important that you deploy ZenML in a way that is accessible from your machine as well as from all stack components that need access to the server.
If you are looking for a quick deployment without having to worry about configuring the right access, the zenml deploy CLI command is the way to go!
Tip: In order to quickly get access to a ZenML server deployed in the cloud without the hassle of setting it up and maintaining it, you can get a free, early version of the ZenML Cloud by filling out this form instead!
Scenario 3: Server and Database hosted on cloud
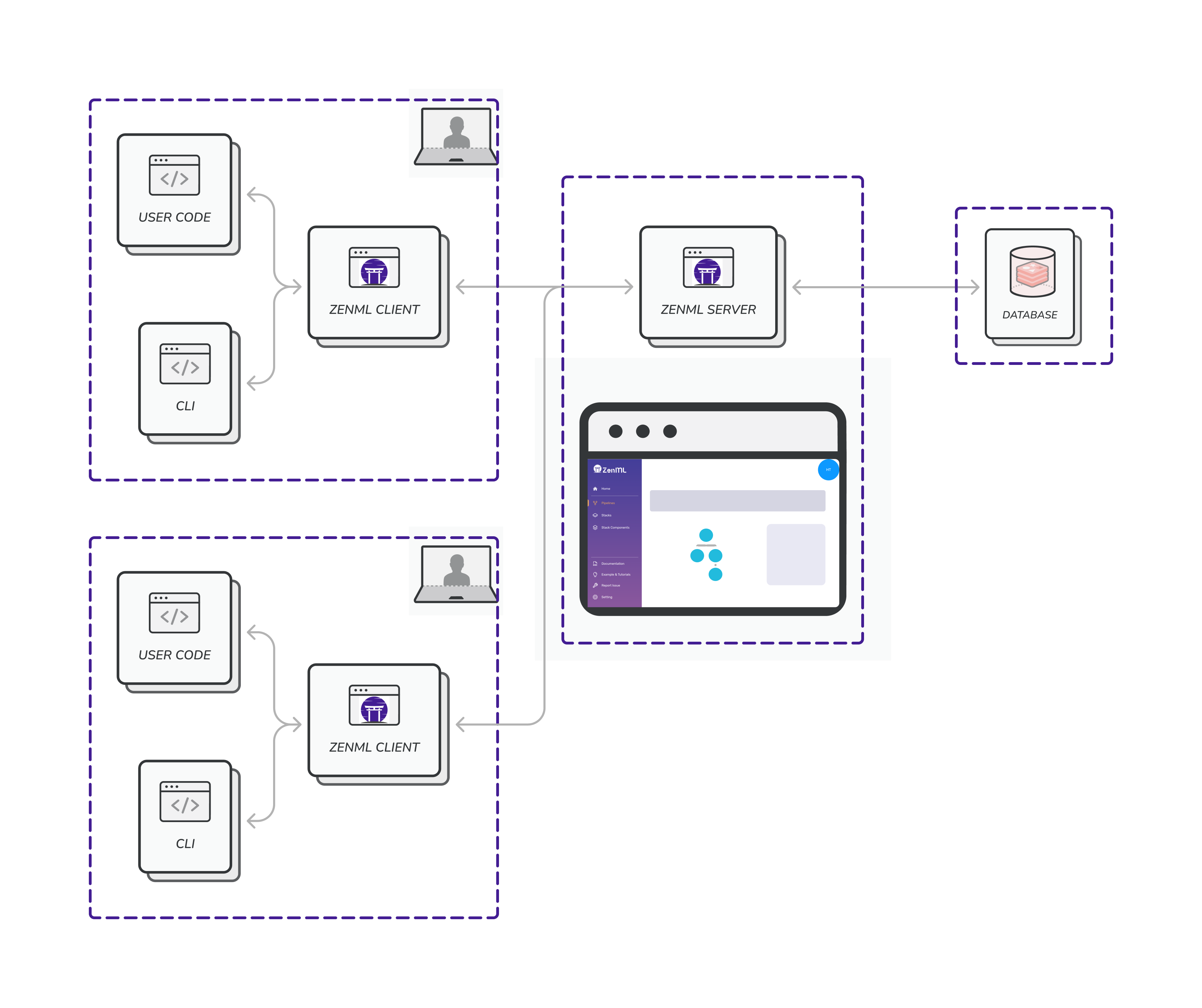
This is similar to Scenario 2, with the difference that both the HTTP server and the database are running remotely rather than on your local machine. This is how you can unleash the real collaborative power of ZenML. With this type of deployment, stacks and pipeline runs can be shared with other users across larger teams and organizations. If you are using cloud, or shared on-premise services to run your pipelines, such as Kubeflow, GitHub, Spark, Vertex AI, AWS Sagemaker or AzureML, a centralized shared ZenML Server is also the recommended deployment strategy for ZenML, because these services will need to communicate with the ZenML server.
The diagram below shows the architecture: both the server and database are remote and can be provisioned and managed independently. The server takes the connection details of the database as one of its inputs and that’s how they work together. You can refer to the deployment options pages, to see how it’s done in each case. Using a cloud deployment enables you to collaborate with your team members by sharing stacks and having visibility into the pipelines run by your team. This new paradigm will also evolve to include more advanced access control features that you can use to manage the roles and responsibilities of everyone in your team through the ZenML Server.
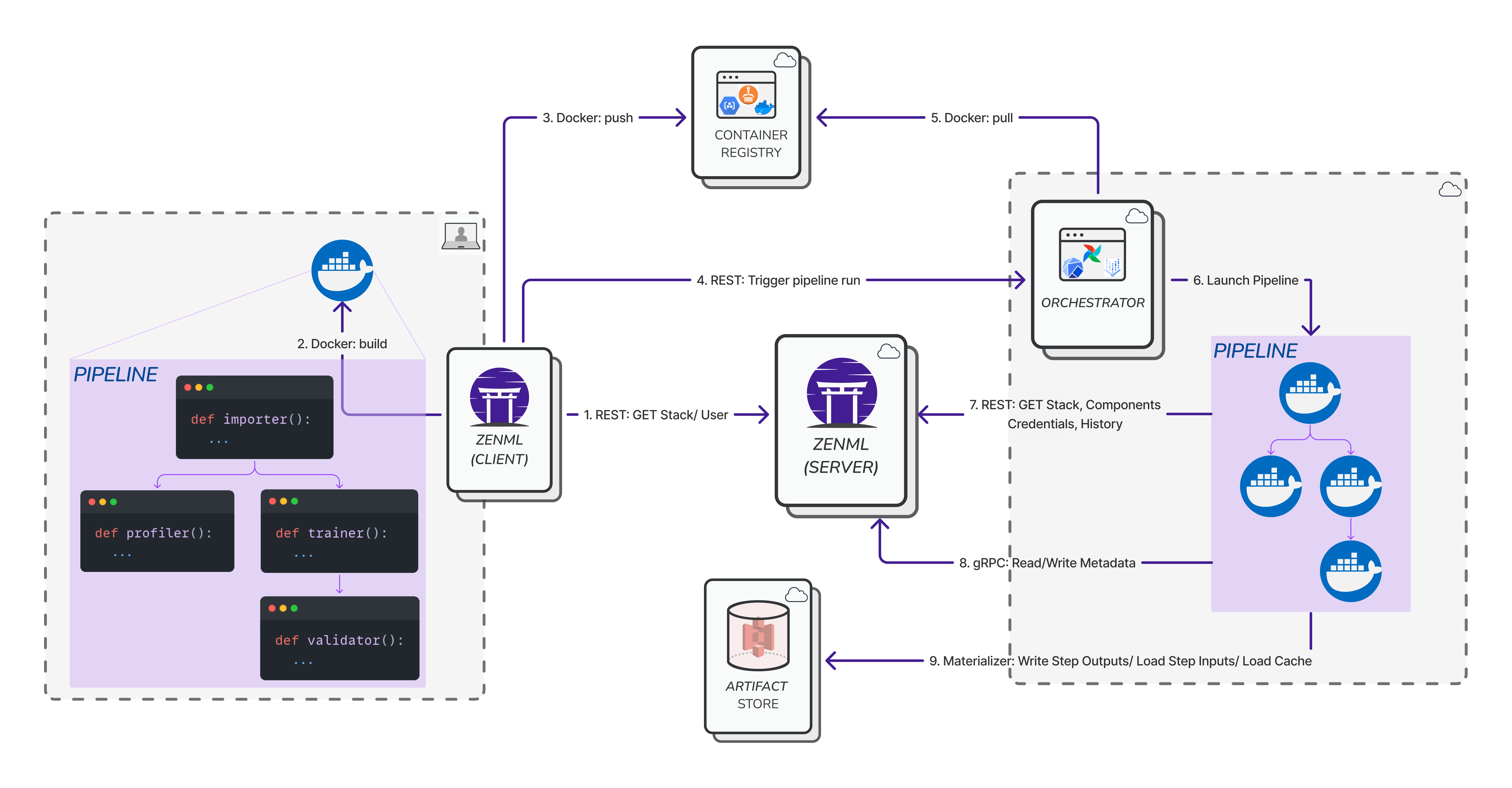
Such a remote deployment unlocks ZenML to its full potential as the MLOps hub within your production stacks. The diagram below visualizes how a pipeline is run through a deployed ZenML Server with a remote orchestrator, artifact store and container registry.
You can use any of the following ways to get started:
- The zenml deploy CLI command that provides an easy interface to deploy on Kubernetes in AWS, GCP or Azure.
- A Docker image that you can run in any environment of your choice.
- A Helm chart that can be deployed to any Kubernetes cluster (on-prem or managed).
In the following pages, we take a look at each of those options.