Managing local stacks (Single-player mode)
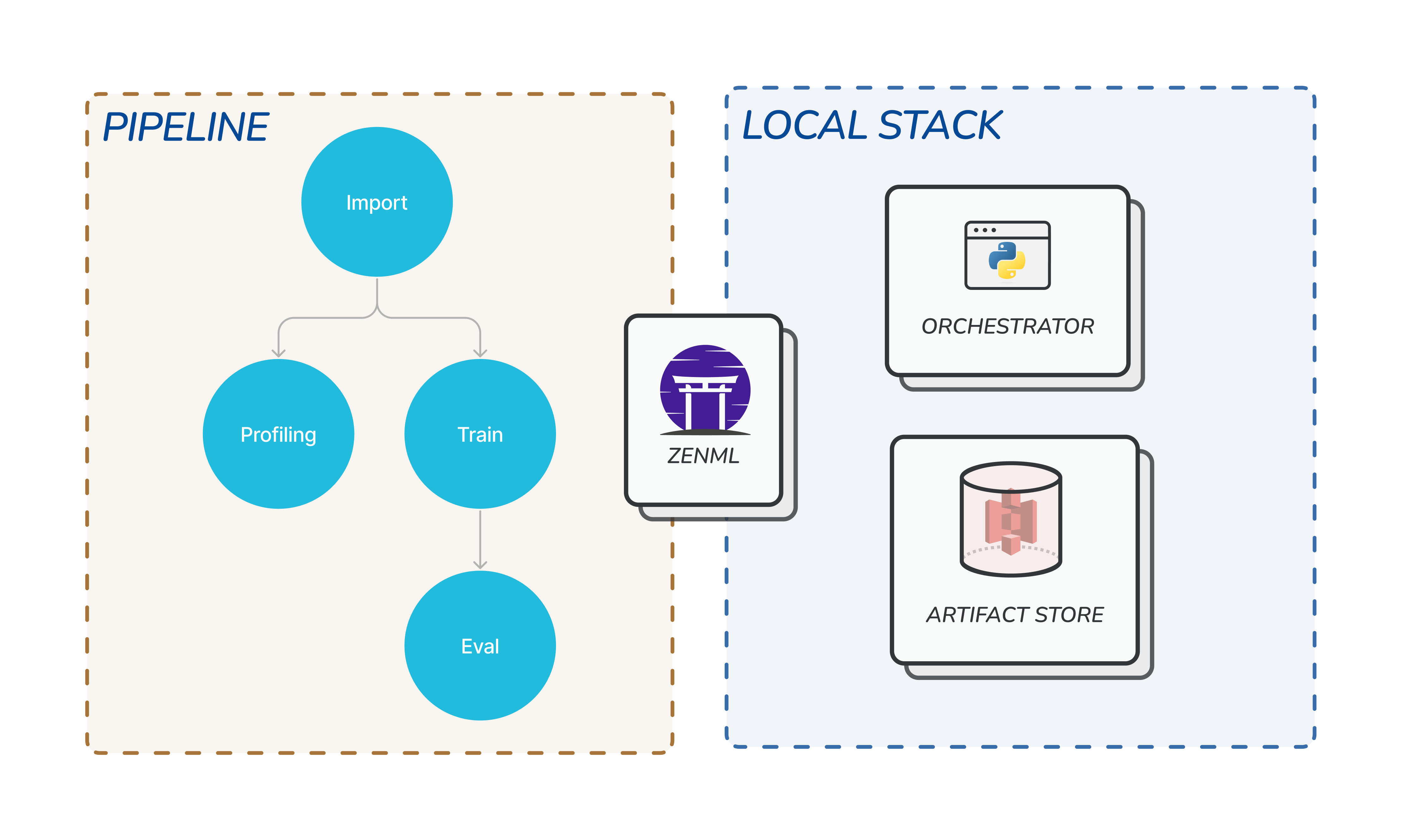
- It is used by ZenML to identify which files must be copied into Docker images in order to execute pipeline steps remotely, e.g., when orchestrating pipelines with Kubeflow.
- It defines the local active Stack that will be used when running pipelines from the repository root or one of its sub-folders.
Registering a Repository
You can register your current working directory as a ZenML repository by running:.zen directory, which contains a single config.yaml file that stores the local settings:
It is recommended to use the
zenml init command to initialize a ZenML Repository in the same location of your custom Python source tree where you would normally point PYTHONPATH, especially if your Python code relies on a hierarchy of modules spread out across multiple sub-folders.ZenML CLI commands and ZenML code will display a warning if they are not running in the context of a ZenML repository, e.g.:Setting the Local Active Stack
One of the most useful features of repositories is that you can configure a different active stack for each of your projects. This is great if you want to use ZenML for multiple projects on the same machine. Whenever you create a new ML project, we recommend you runzenml init to create a separate repository, then use it to define your stacks:
Detailed Example
Detailed usage example of local stacks
Detailed usage example of local stacks
The following example shows how the active stack can be configured locally for a project without impacting the global settings:
zenml stack register mystack ... --share) or afterwards (e.g. through zenml stack share mystack).
To differentiate between shared and private Stacks and Stack Components, these can now be addressed by name, id or the first few letters of the id in the cli. E.g. for a stack default with id 179ebd25-4c5b-480f-a47c-d4f04e0b6185 you can now run zenml stack describe default or zenml stack describe 179 or zenml stack describe 179ebd25-4c5b-480f-a47c-d4f04e0b6185.
We also introduce the notion of local vs non-local stack components. Local stack components are stack components that are configured to run locally while non-local stack components are configured to run remotely or in a cloud environment. Consequently:
- stacks made up of local stack components should not be shared on a central ZenML Server, even though this is not enforced by the system.
- stacks made up of non-local stack components are only functional if they are shared through a remotely deployed ZenML Server.
Viewing the dashboard
While in single-player mode, you can still use the dashboard. ZenML natively supports running the HTTP server and dashboard either as a process running in the background. By default, thezenml up command starts the HTTP server as a local daemon process that uses the same database configuration as your local client. A URL is provided where the ZenML Dashboard can be loaded to show your available stacks, pipeline runs and team settings among other things.
zenml down does the opposite and spins the process down. You can read more about this here.
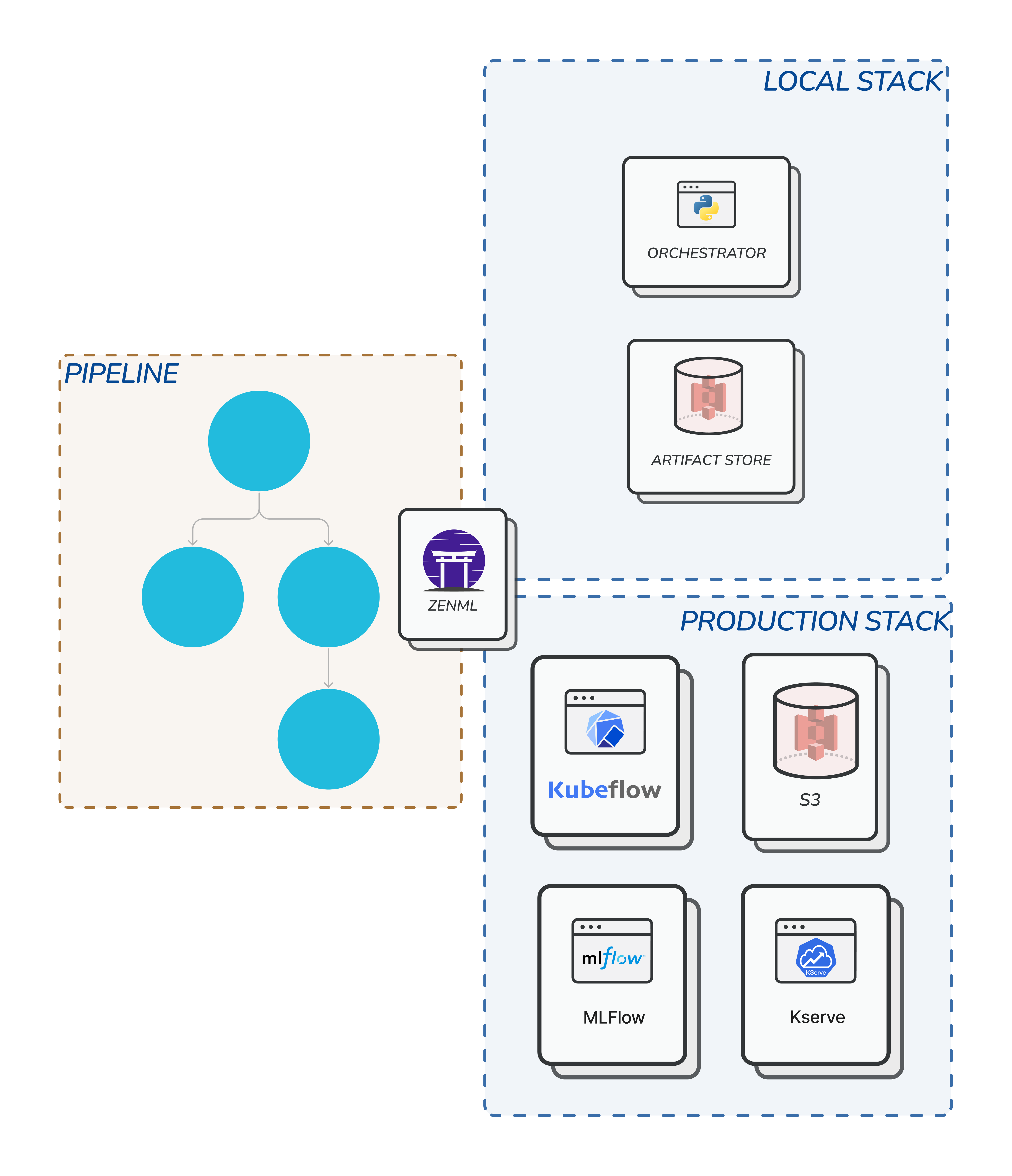
Managing Remote Stacks (Multi-player mode)
If you are working in a non-local, collaborative setting, then the first question you would ask is how to share pipelines and stacks with other people. There are two answers to this question:Export and Import Stacks
If you wish to transfer one of your stacks to another user or even another machine, you can do so by exporting the stack configuration and then importing it again. To export a stack to YAML, run the following command:Known Limitations
The exported Stack is only a configuration. It may have local dependencies that are not exported and thus will not be available when importing the Stack on another machine:- the secrets stored in the local Secrets Managers
- any references to local files and local services not accessible from outside the machine where the Stack is exported, such as the local Artifact Store.
- perhaps critically, the exported stack would not contain any pipelines or pipeline runs. For that you need to set up a ZenML Server (see section below).
Sharing stacks over a ZenML Server
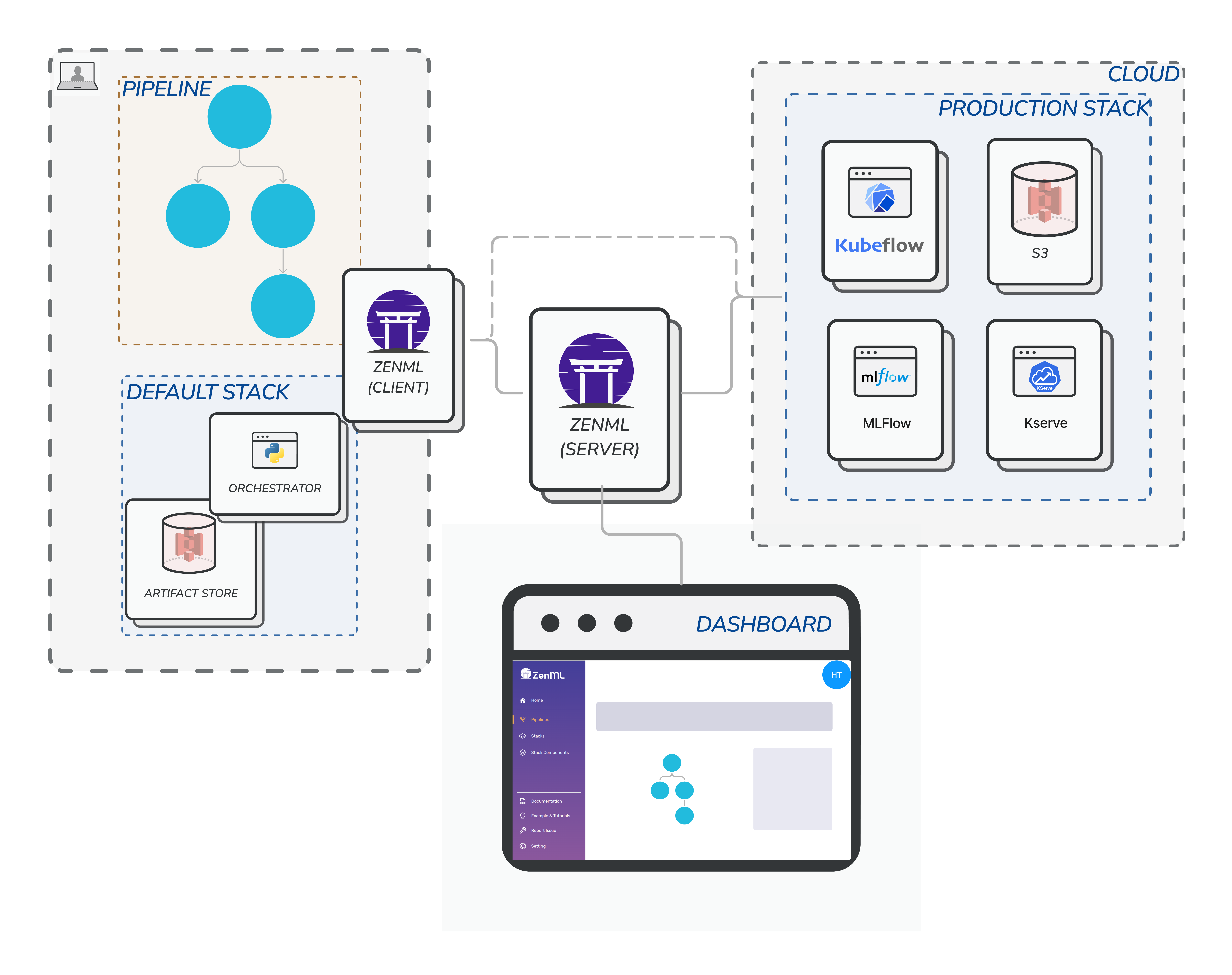
default with id 179ebd25-4c5b-480f-a47c-d4f04e0b6185 you can run:
local vs non-local stack components.
- Local stack components are stack components that are configured to run locally
- Non-local stack components are configured to run remotely or in a cloud environment.
- Stacks made up of local stack components should not be shared on a central ZenML Server, even though this is not enforced by the system.
- Stacks made up of non-local stack components are only functional if they are shared through a remotely deployed ZenML Server.

